Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light
Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light: According to the law of energy conservation, energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Consequently, when a photon of light is absorbed by matter, usually by an atom, molecule, or ion or by a small grouping of such units, the photon disappears and its energy is gained by the matter. Similarly, when matter emits light, it loses the energy carried away by the photons. A given atom or molecule cannot emit light of any arbitrary energy, since quantum theory explains that only certain energy states are possible for a given system.
Color, the aspect of any object that may be described in terms of hue, lightness, and saturation. In physics, color is associated specifically with electromagnetic radiation of a certain range of wavelengths visible to the human eye. Learn more about color in this article.

How the Fruits Got Their Colors – Sustainable Nano
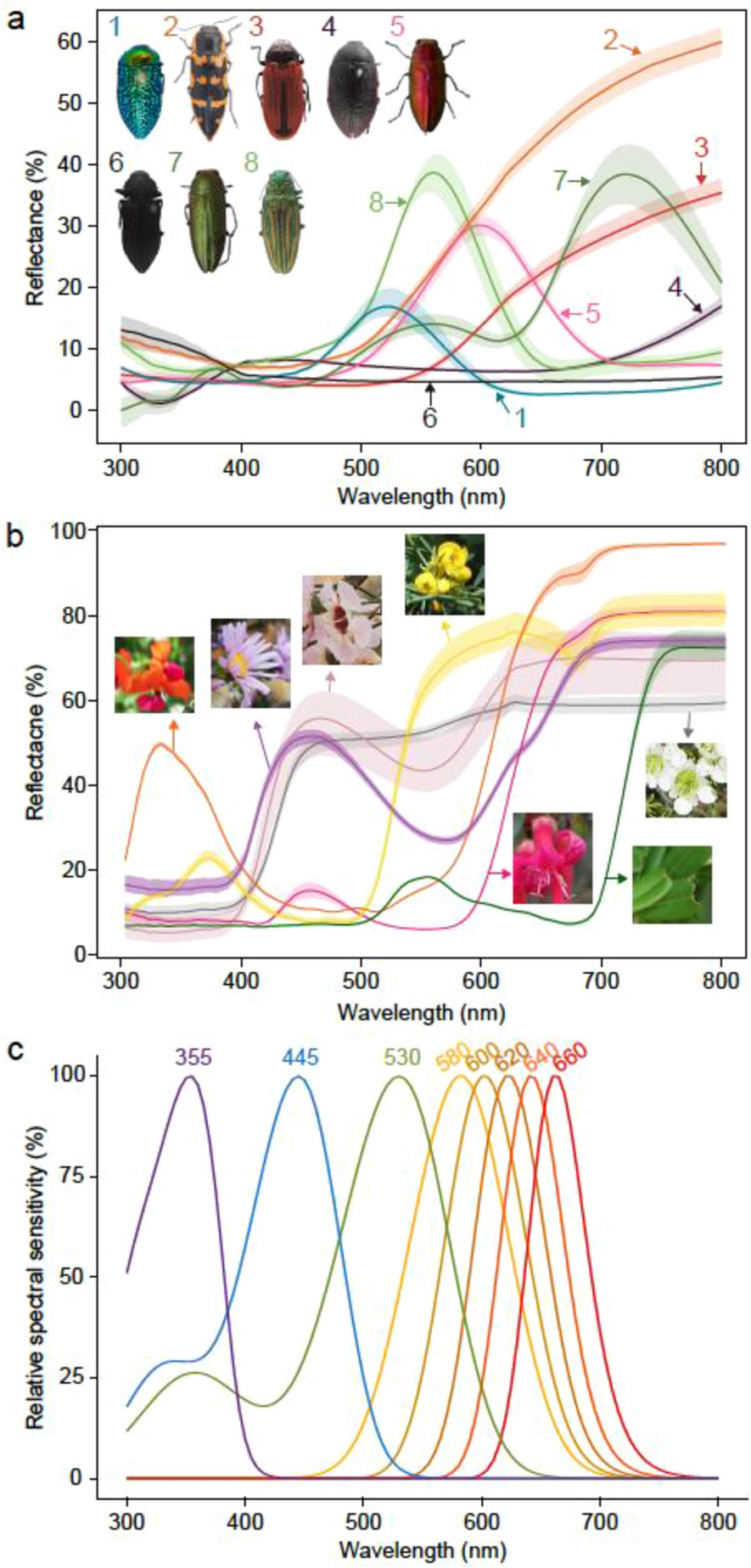
Insect visual sensitivity to long wavelengths enhances colour contrast of insects against vegetation
Color Mixing

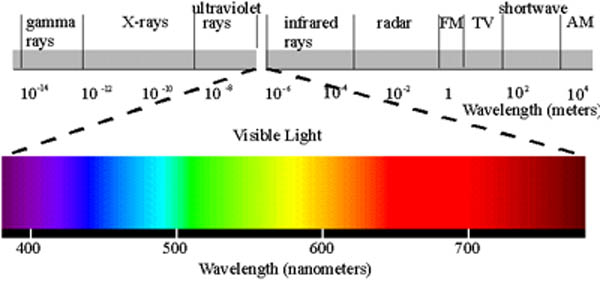
Visible Light Spectrum Wavelengths and Colors
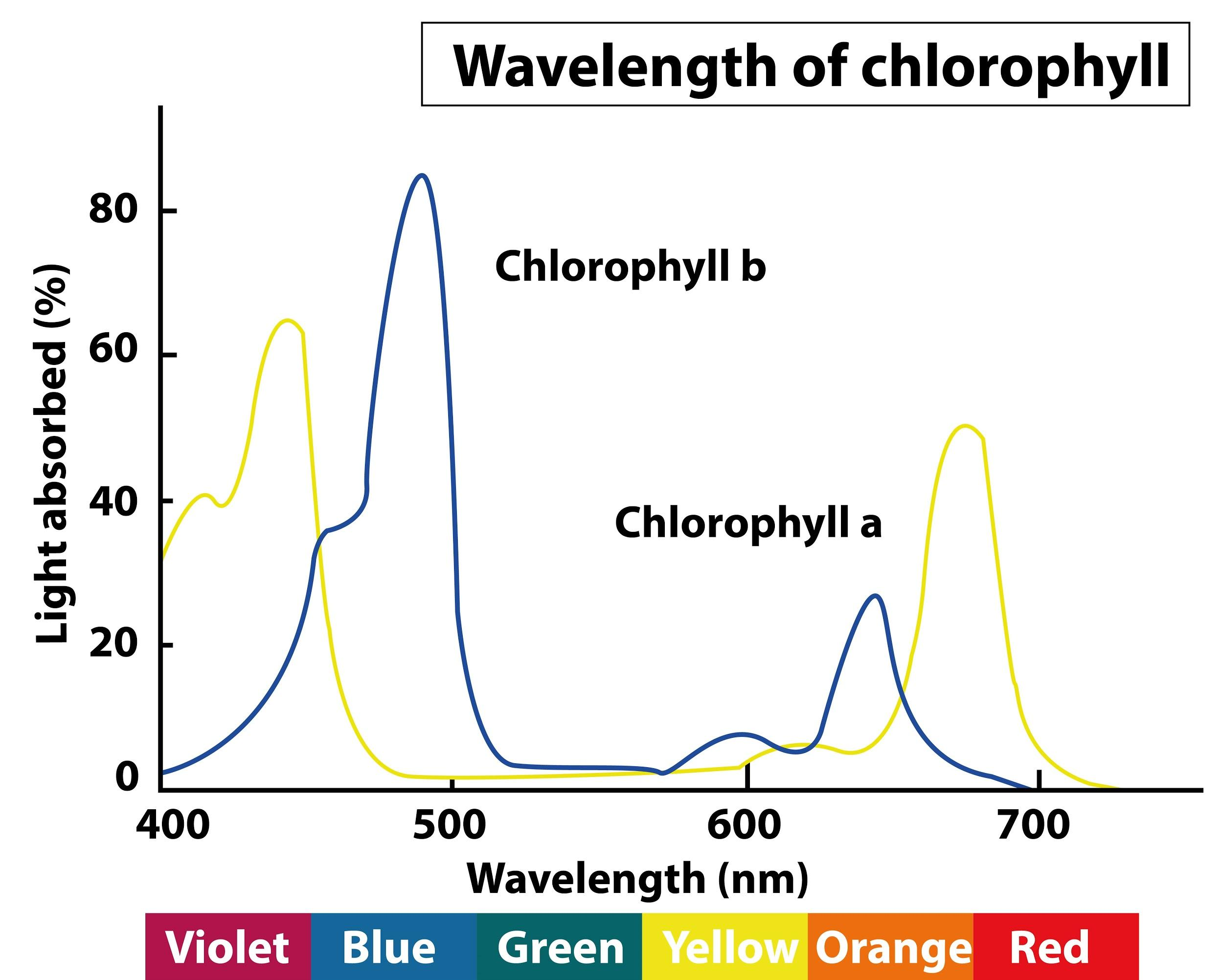
Chlorophylls absorbs visible light of wavelength(a) 400 - 500 nm only(b) 300 - 400 nm only(c) 600 - 800nm only(d) 400 - 500 nm and 600 - 700 nm

Absorption range of different algae pigments, including chlorophyll a
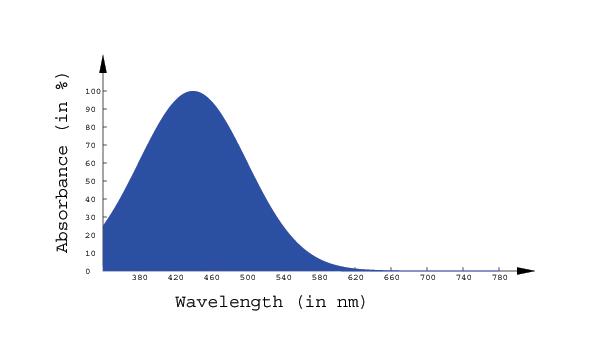
Math 309 Project: Colour Vision
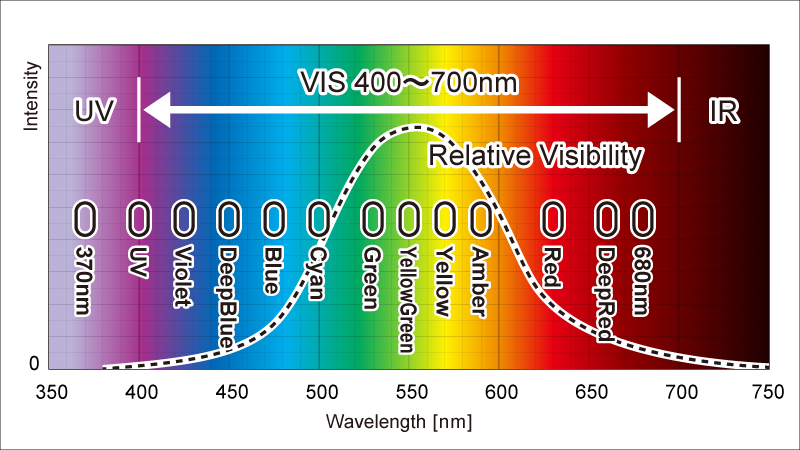
Coral Color Management|BlueHarbor

Compound Interest: Inorganic Pigment Compounds – The Chemistry of Paint

Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light
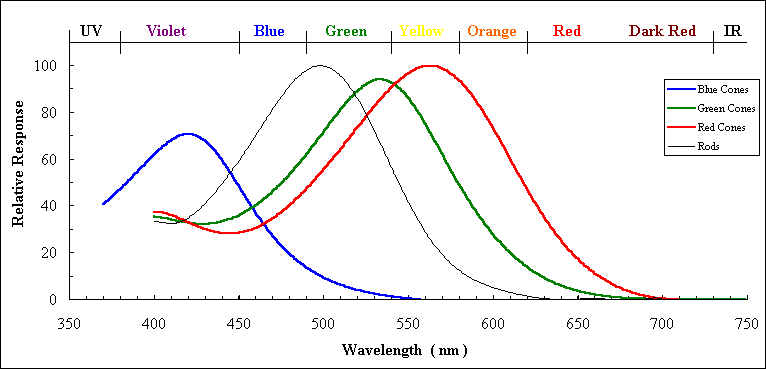
Cone Action Spectra

Biology Notes for A level: #101 Photosynthetic Pigments