Steel - Casting, Alloy, Heat Treatment
Steel - Casting, Alloy, Heat Treatment: The simplest way to solidify liquid steel is to pour it into heavy, thick-walled iron ingot molds, which stand on stout iron plates called stools. During and after pouring, the walls and bottom of the mold extract heat from the melt, and a solid shell forms, growing approximately with the square root of time multiplied by a constant. The value of the constant depends on the heat flux between the already solidified shell and the cooling media surrounding it and is actually equivalent to the solidified shell’s thickness after one minute—namely, about 20 millimetres when solidifying steel. Accordingly, the ingot
Steel, alloy of iron and carbon in which the carbon content ranges up to 2 percent (with a higher carbon content, the material is defined as cast iron). By far the most widely used material for building the world’s infrastructure and industries, it is used to fabricate everything from sewing needles to oil tankers.
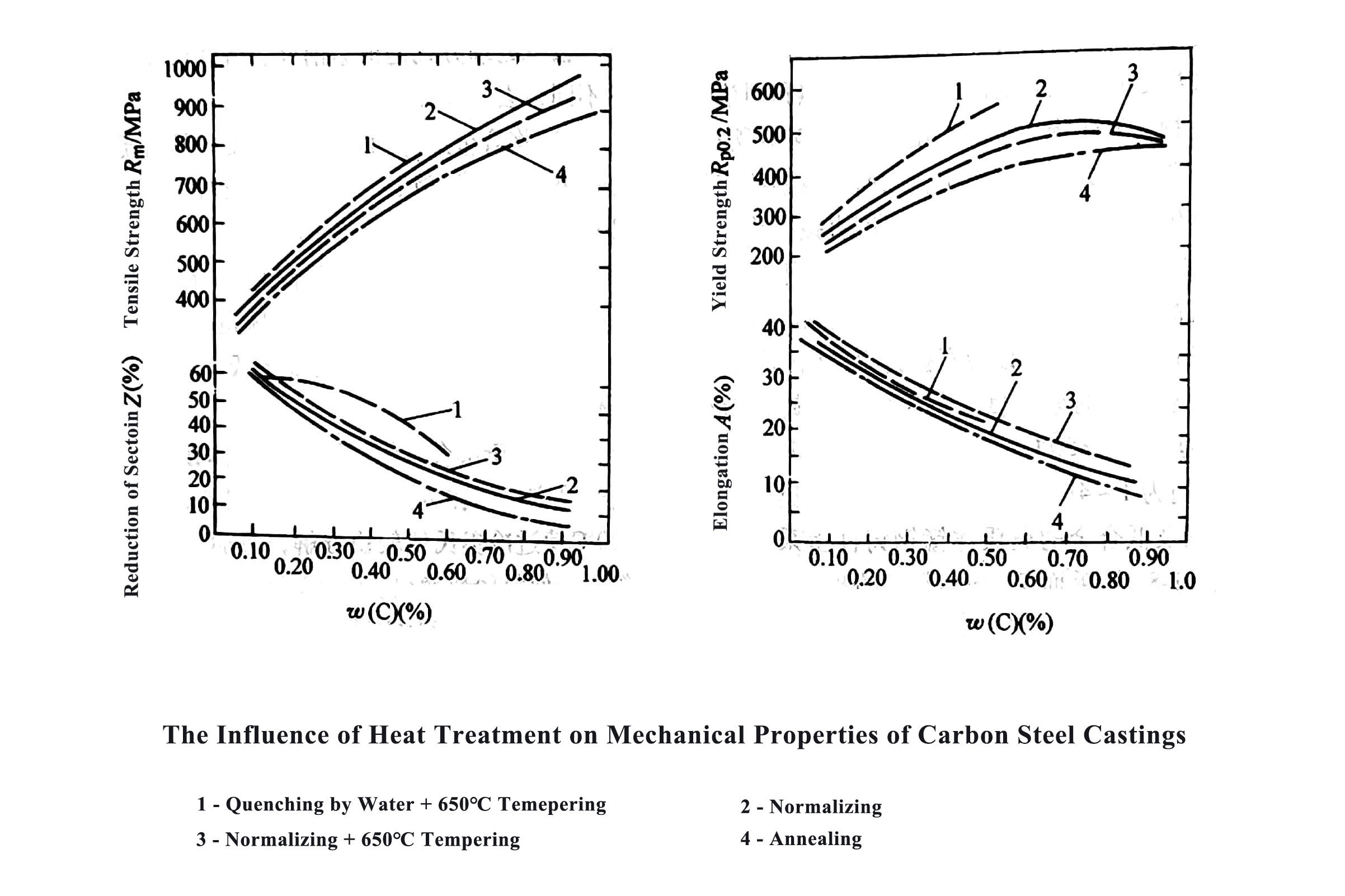
General Information of Heat Treatment for Steel Castings, Investment Casting Company

Materials, Free Full-Text
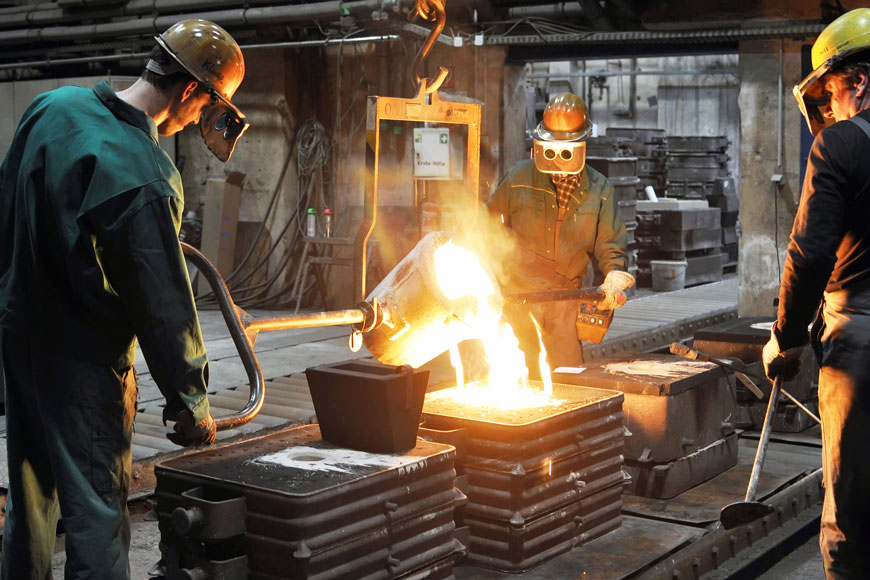

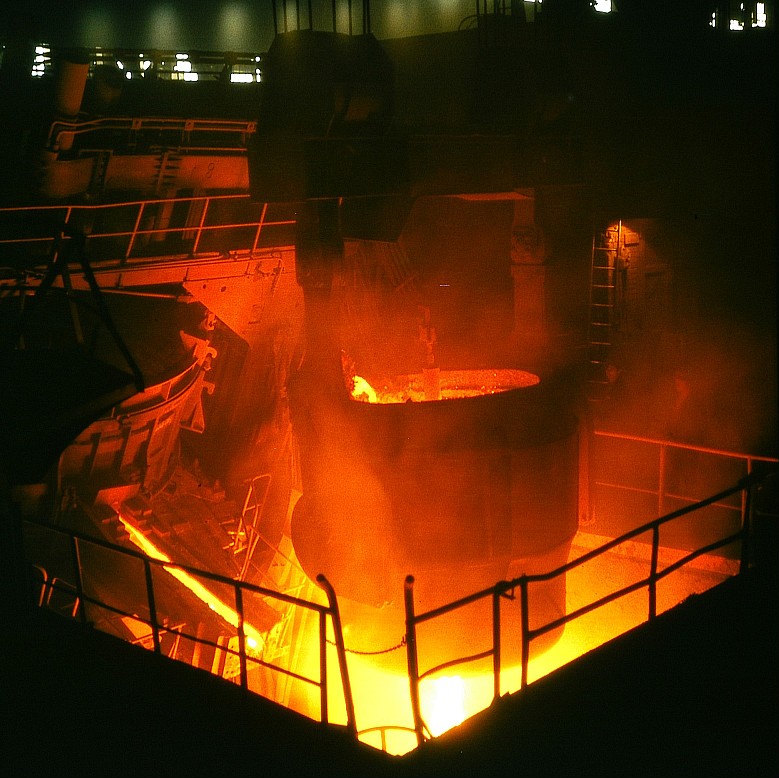
Cast Steel Production
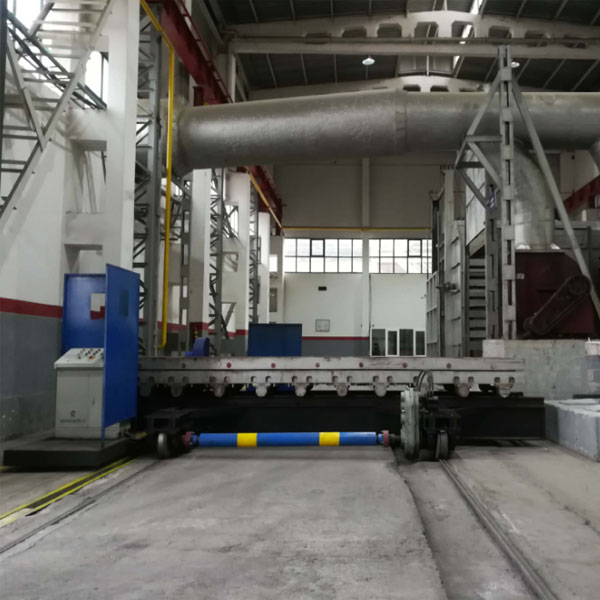

Heat Treatment for Die Casting Aluminum Alloy

Heat Treatment
Microstructures of alloy 360 for the as-cast and each of the
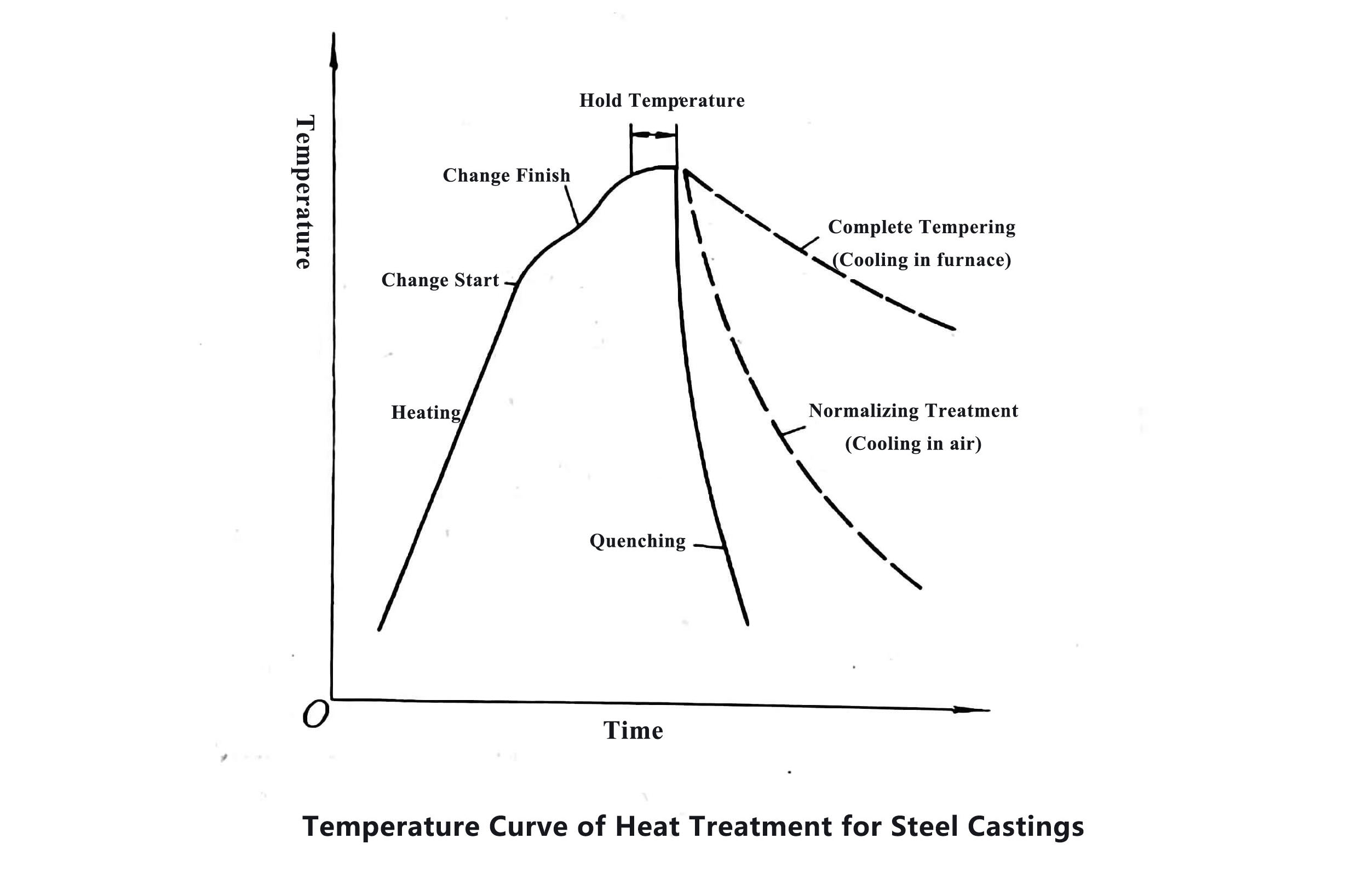
General Information of Heat Treatment for Steel Castings, Investment Casting Company

How heat treatment helps your iron casting perform its best - The C.A. Lawton Co.
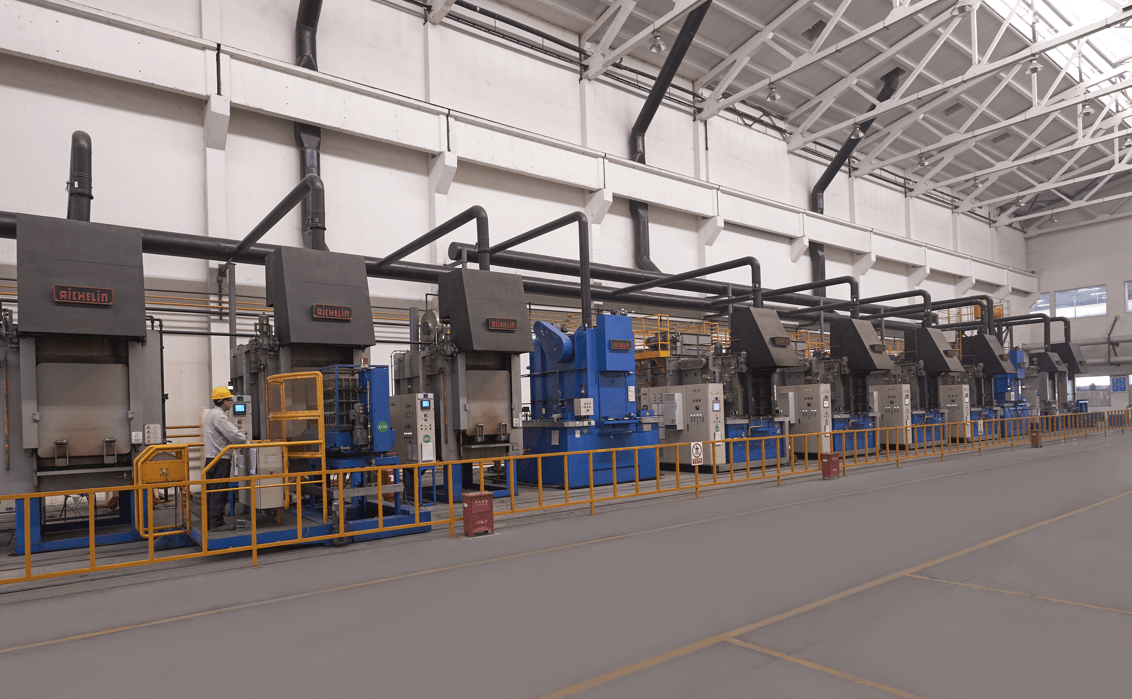

Heat Treatment of Investment Castings Parts

Effects of heat treatment and addition of small amounts of Cu and Mg on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Cu and Al-Si-Mg cast alloys - ScienceDirect

Heat Treatment for Metals - MetalTek

The 4 Types of Heat Treatment Steel Undergoes

Best Aluminum Heat Treatment Furnace manufacturers India Aluminum Hardening Furnace and Aging Ovens manufacturer Mumbai, Pune, Hyderabad, Delhi, Bengaluru, Kolkata, T6 Treatment furnace

Heat Treatment Process for Metal Casting: Why it is so important?