What is the formula for p- and s-waves in an earthquake?
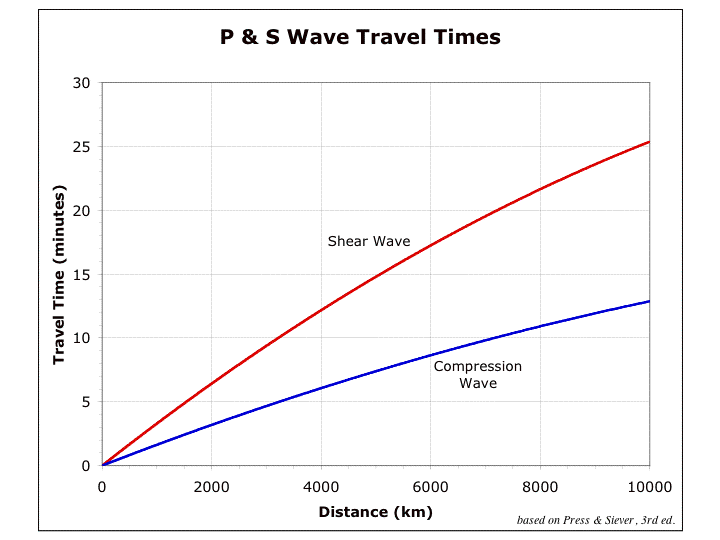
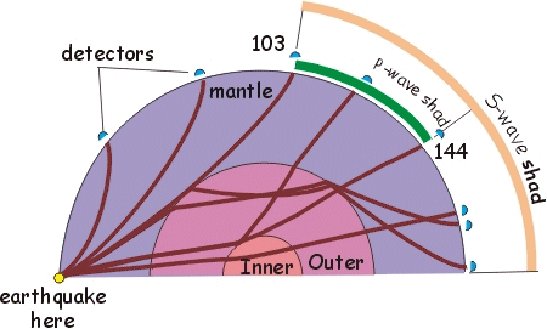
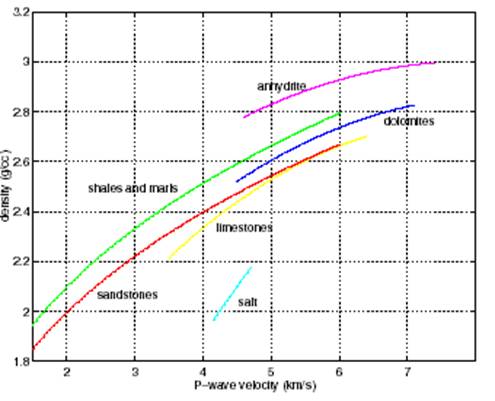
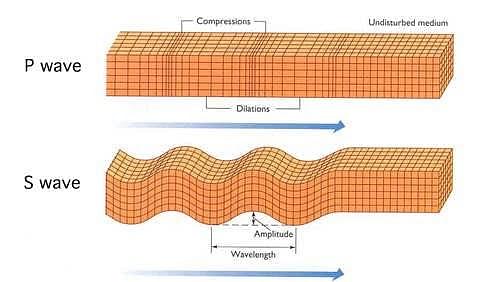
Depends on what you mean by the term of 'formula'. There are more than one way to explain this question. For instance velocity of the P and S waves are as below, respectively: α^2 =(λ + 2µ)/ρ β^2 =µ/ρ ρ is the density of the material through which the wave propagates . µ is the shear modulus which describes the material's response to shear stress. λ is he first Lame parameter. Velocity of these waves are different from each other. Their differences can be seen in the graph below. Compression wave and shear wave are representing P and S wave, respectively. The other way is to detect their arrival to seismic station. For instance if you know the distance between earthquake's location and the location of the seismic station. You can calculate P and S wave arrivals as below: d = t (S-P)*8 d = t (S-P)*10 First formula is used by local earthquakes (epicentral distance: 0-500 km) and the second one is used for regional earthquakes (epicentral distance: up to 1000 km).
EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY I
EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY I
P Wave: Types, Properties and Velocity

Seismic wave - Wikipedia
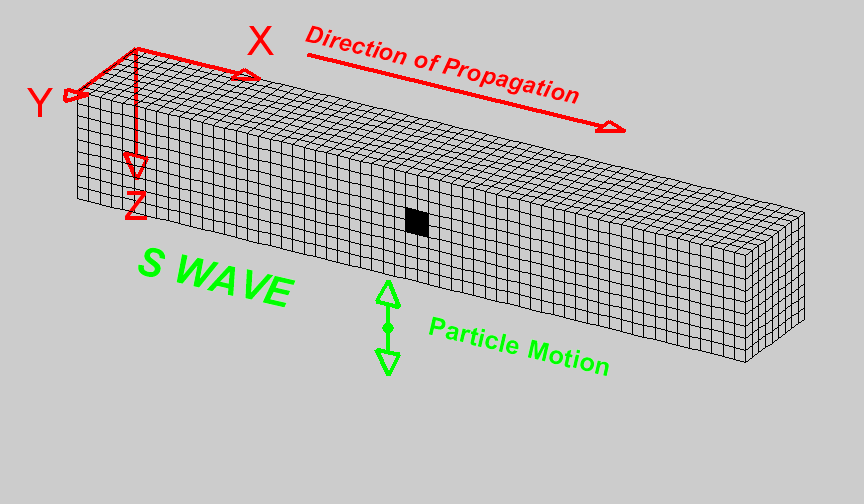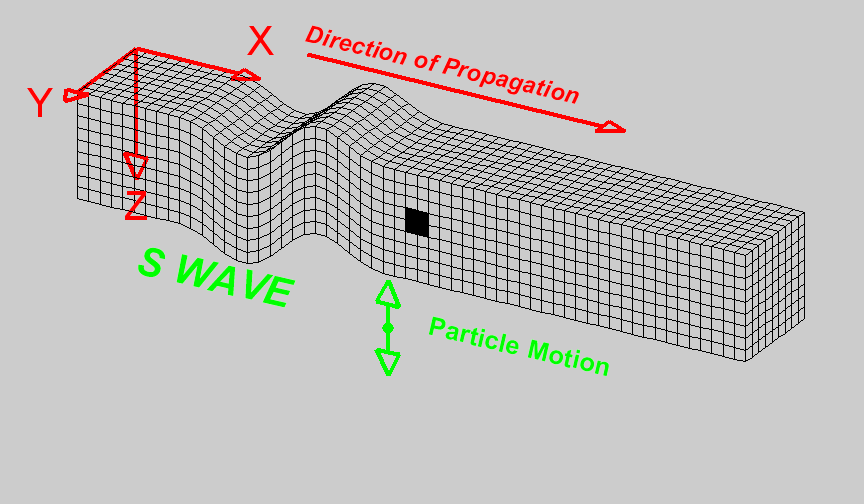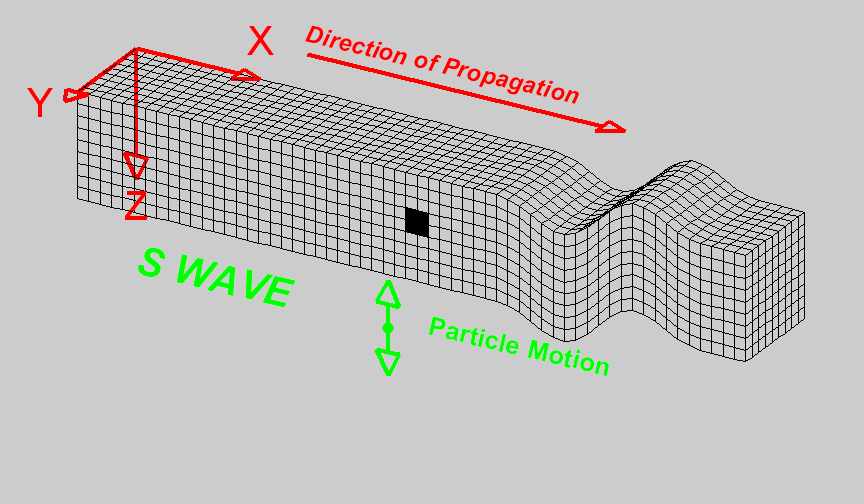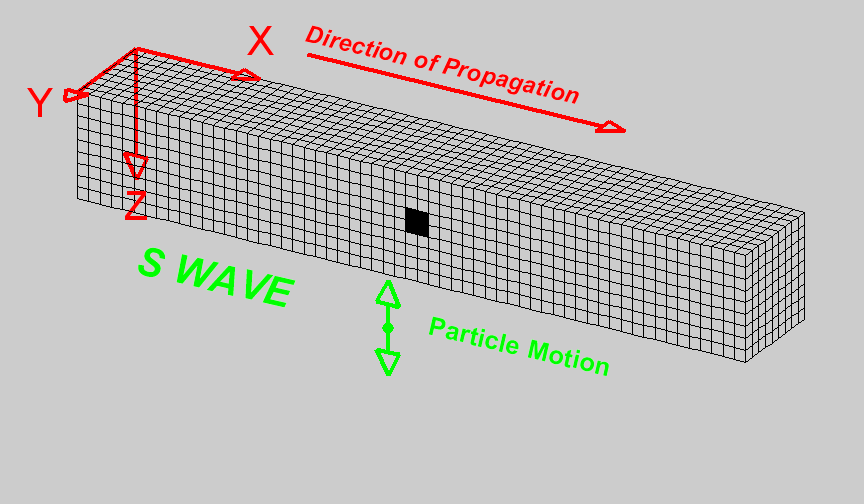
Basics of wave propagation — GPG 0.0.1 documentation

Frontiers Applicability of On-Site P-Wave Earthquake Early Warning to Seismic Data Observed During the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake, Japan
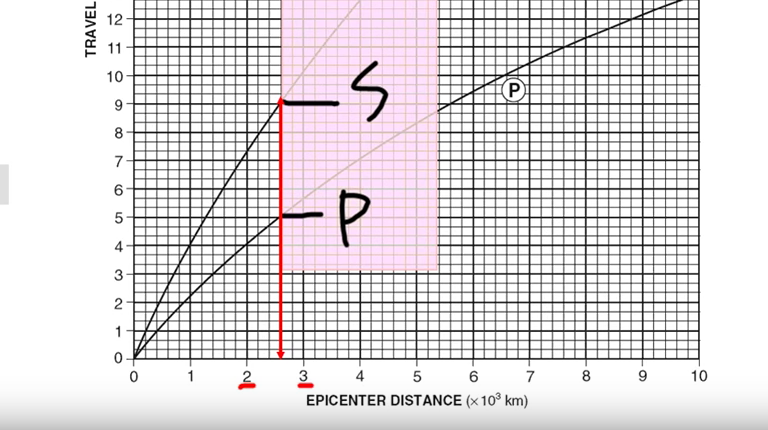
How to Find the Epicenter of an Earthquake
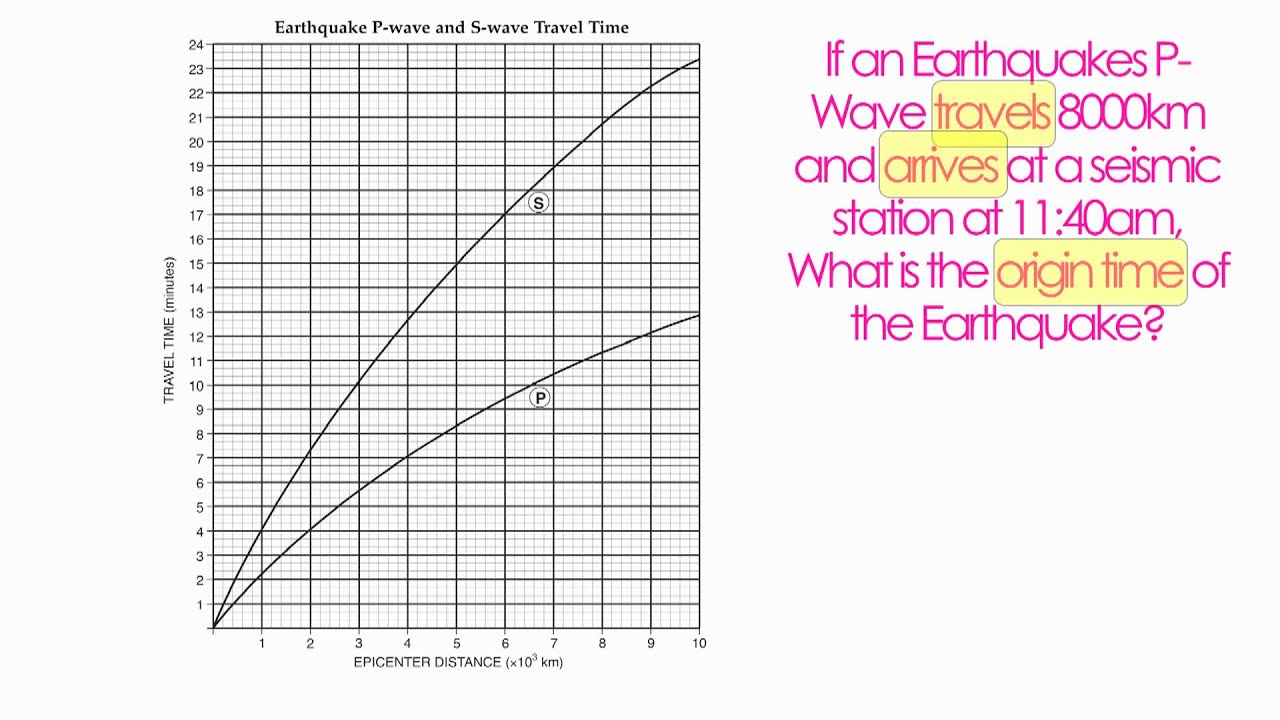
Earth Science Reference Table Pg 11 - P and S Wave Chart-Hommocks Earth Science Department

A typical time variation for P-and S-waves.
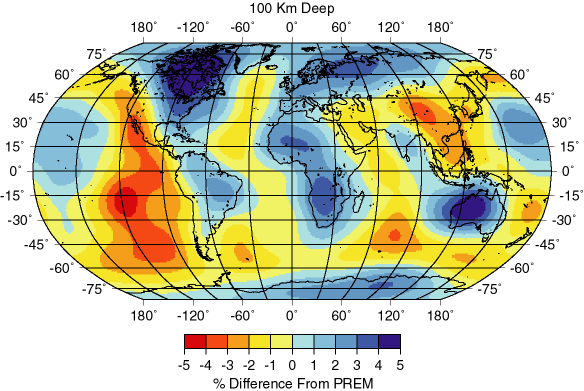
Seimic Waves and Earth's Interior
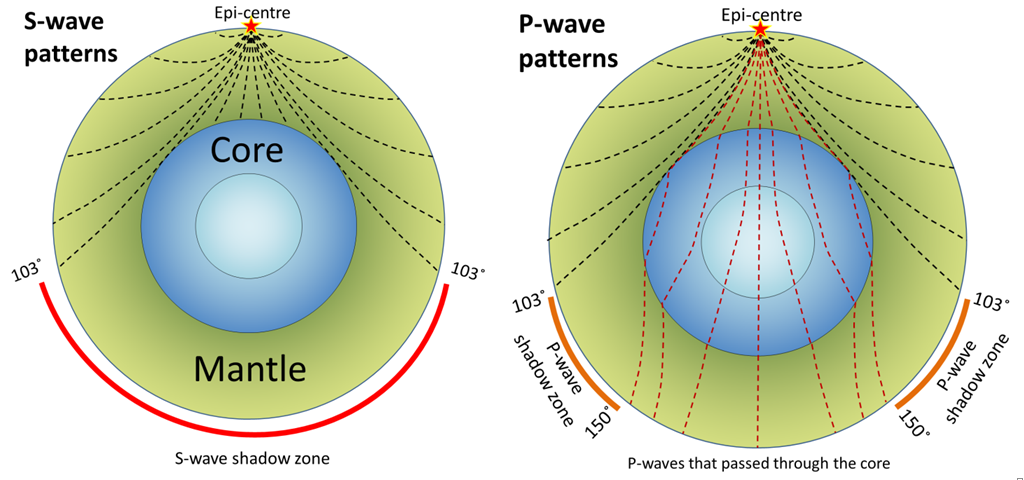
5.3 Measuring and Locating Earthquakes – Dynamic Planet: Exploring Geological Disasters and Environmental Change

Understanding the Fundamentals of Earthquake Signal Sensing Networks